For greater than 40 years, america—a nation that putatively cherishes freedom—has had one of many largest jail programs on the planet. Mass incarceration has been so persistent and pervasive that reform teams devoted to lowering the jail inhabitants by half have usually been derided as made up of fantasists. However the subsequent decade may see this aim met and exceeded: After peaking at simply greater than 1.6 million Individuals in 2009, the jail inhabitants was simply greater than 1.2 million on the finish of 2023 (the newest yr for which knowledge can be found), and is on monitor to fall to about 600,000—a decline of roughly 60 p.c.
Discerning the approaching prison-population cliff requires understanding the connection between crime and incarceration over generations. A metropolis jail presents a snapshot of what occurred final night time (for instance, the gang’s football-victory celebration turned ugly). However a jail is a portrait of what occurred 5, 10, and 20 years in the past. Center-aged individuals who have been law-abiding their entire life till “one thing snapped” they usually dedicated a horrible crime are a staple of crime novels and films, however in actual life, just about everybody who results in jail begins their prison profession of their teenagers or younger maturity. As of 2016—the newest yr for which knowledge can be found—the common man in state jail had been arrested 9 instances, was at present incarcerated for his sixth time, and was serving a 16-year sentence.
Due to that elementary dynamic, the reason for why roughly 1.6 million folks—greater than 500 for each 100,000 Individuals—had been in a state or federal jail in 2009 has little or no to do with what was occurring on the streets or with law-enforcement insurance policies that yr. Somewhat, the causes lay within the closing many years of the twentieth century.
From the tip of World Battle II till the mid-Seventies, the proportion of Individuals in jail every year by no means exceeded 120 per 100,000. However beginning within the late Sixties, a multidecade crime wave swelled in America, and an unprecedented variety of adolescents and younger adults had been criminally energetic. In response, the anti-crime insurance policies of most native, state, and federal governments turned increasingly more draconian. The mixed end result was that the jail inhabitants exploded. By 1985, the imprisonment fee had doubled from its historic norm, such that greater than 200 in 100,000 Individuals had been in a state or federal jail. The variety of folks in jail elevated a mean of 8 p.c a yr for the following decade, breaching the 1 million mark in 1994 and persevering with to develop till 2009. This had ramifications that had been felt for years: As a result of most people who find themselves launched from jail return, the system has been stocked and restocked with the legacy of that American crime-and-punishment wave for 1 / 4 century. That’s why the 2009 peak of U.S. imprisonment got here 18 years after the 1991 peak within the violent-crime fee. The jail system is sort of a badly overloaded tractor trailer—it takes a very long time to cease even after the brakes are hit.
That tractor trailer is lastly slowing down, many years after the “nice crime decline” started within the Nineties. Till 2009, the lengthier sentences handed down throughout the previous crime wave and the tendency of launched prisoners to be re-incarcerated saved imprisonment rising whilst crime declined. However the falling crime that the U.S. skilled within the Nineties and 2000s is now lastly translating right into a shrinking jail inhabitants.
This chart, utilizing knowledge from the U.S. Division of Justice, exhibits the collapse of prison arrests of minors within the twenty first century. Quickly declining numbers of youth are committing crimes, getting arrested, and being incarcerated. This issues as a result of younger offenders are the uncooked materials that feeds the jail system: As one technology ages out, one other takes its place on the identical horrid journey. The U.S. had a particularly high-crime technology adopted by a lower-crime technology, which means that the older inhabitants shouldn’t be being changed at an equal fee. The influence of this shift on the jail inhabitants started greater than a decade in the past however has been little seen as a result of it takes so lengthy for the large jail inhabitants of longer provenance to clear.
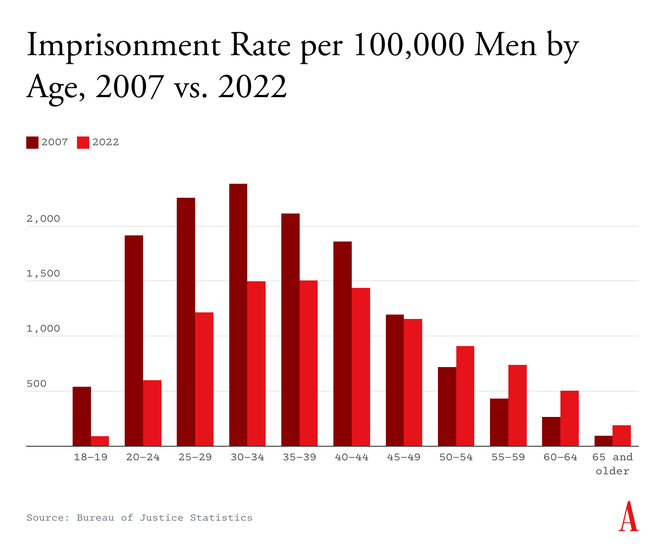
However such a metamorphosis is now nicely beneath manner. One statistic vividly illustrates the change: In 2007, the imprisonment fee for 18- and 19-year-old males was greater than 5 instances that of males over the age of 64. However immediately, males in these usually crime-prone late-adolescent years are imprisoned at half the speed that senior residents are immediately.
Because the snake digests the pig yr after yr, the American jail system is solely not going to have sufficient inmates to justify its continued measurement or staggering prices. Some states which might be considering increasing their jail capability will probably be losing their cash—their services will probably be overbuilt and underused. By 2035, the general imprisonment fee might be as little as 200 per 100,000 folks. States ought to as a substitute be tearing down their most deteriorated and inhumane correctional services, assured that they won’t want the area.
This optimistic evaluation may have been written in 2019, when the imprisonment fee had been falling for greater than a decade and hit a stage not seen since 1995. I considered writing this text then, however a world turned the wrong way up shook my confidence.
COVID initially appeared like a boon for decarceration as a result of states diminished jail admissions and accelerated releases in 2020 to cut back transmission, chopping the jail inhabitants by 16 p.c. However whether or not it was on account of this mass launch, COVID, de-policing, different components, or some mixture thereof, crime exploded in 2020 after a protracted quiescent interval, most shockingly with an unprecedented 30 p.c improve in homicides. Crime spikes improve incarceration straight as a result of extra persons are committing crimes and likewise as a result of they lead the general public to demand extra aggressive insurance policies, which frequently translate into longer and extra frequent jail sentences. If the turmoil of the early 2020s had led to an prolonged interval of excessive crime and excessive punishment much like what the U.S. skilled within the late twentieth century, the COVID-era contraction of the jail inhabitants may have been instantly nullified after which some when, within the ensuing years, the jail pipeline was finally replenished.
However fortunately, the spike was only a spike, not a brand new equilibrium. Crime stopped rising someday in 2022, and fell in 2023 and 2024. The jail inhabitants inched up 2 p.c in 2022 and once more in 2023, and it’s potential {that a} comparable rise came about in 2024, however even collectively, it is a fraction of the sudden inhabitants decline throughout the early pandemic. The COVID period ended with jail populations decrease moderately than increased: A current Vera Institute report discovered that, on stability, from 2019 to the spring of 2024, the variety of federal prisoners declined by 11 p.c, and the variety of state prisoners declined by 13 p.c.
Accelerating the de-prisoning of America is worth it and potential. The advantages of a smaller jail inhabitants aren’t restricted to those that would in any other case be locked up and the individuals who love them. Prisons crowd out different coverage priorities that many citizens would love the federal government to spend more cash on. In all 50 states, the associated fee to imprison somebody for a yr considerably exceeds the price of a yr of Ok–12 training. However even larger than the monetary financial savings could be the prosperity in human phrases: Much less crime and fewer incarceration are profound blessings for a society.
The best accessible coverage to speed up the decarceration development is to cease constructing prisons besides in circumstances the place a smaller, fashionable facility is changing a bigger, decaying establishment. Although it is going to be nonintuitive to many reformers, notably on the left, opposition to any such new services being personal needs to be dropped. The principal political barrier to closing half-full prisons is the facility of public-sector unions. In distinction, a personal jail might be despatched to its reward if its contract is canceled. Particular person communities in areas of low employment may even combat to maintain their prisons. Jail-closing commissions, analogous to military-base-closing commissions, could also be needed and may coordinate with legislators to offer employee retraining and monetary help to compensate for the lack of high-wage jobs in communities whose economic system revolves round corrections.
Lastly, America mustn’t let its jail system develop into the costliest and inhumane of nursing properties. The speed of recidivism amongst senior residents is close to zero, and compassionate launch of sick and growing older inmates needs to be the default moderately than the exception, a reversal of present follow.

In any given future yr, small rises in imprisonment are potential, however the macro development is ineluctable: Society goes to expertise the advantages of previous many years of decrease crime all through its jail system. The imprisonment fee will probably be decrease in 5 years and decrease nonetheless in 10. Prisons will nonetheless exist then and nonetheless be wanted, however the fee at which Individuals are confined in them might be decrease than something within the previous half century. That is the fruit of a lower-crime society—good in and of itself, certainly, notably for the low-income and majority-minority communities the place most crime happens. It’s going to additionally, after all, be a blessing for individuals who keep away from jail, and for the taxpayers who not need to pay for it. The decline within the jail inhabitants will probably be one thing everybody in our polarized society could have purpose to rejoice.

